The Future Depends on our Ability to Adapt: Adaptive Multi-paddock Grazing
17/09/2020
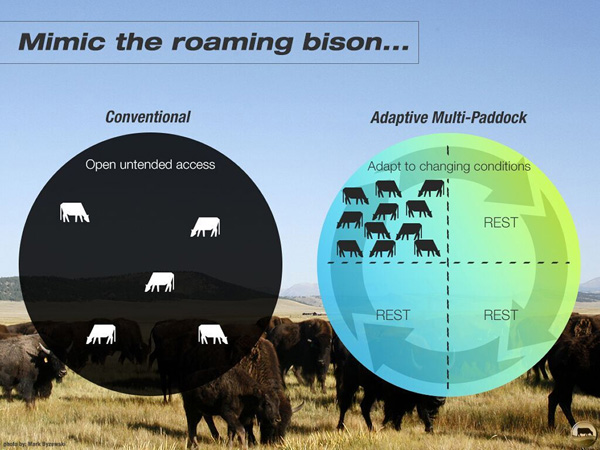
Image source: http://standardsoil.com/our-approach/amp-grazing/
Adaptive Multi-Paddock (AMP) grazing uses high livestock densities for short durations, between long periods of forage rest, to catalyse accelerated grass growth. When intensively grazing small paddocks for a brief duration, any management mistakes are limited to very small areas. The system is highly observant and adaptive, based on reading the conditions of the land and forage, assessing the needs of the livestock, and planning the grazing appropriately. It mimics the natural pattern of dense herds of wild ruminants moved frequently by the forces of predation and food availability.
When grass is left to grow, as the season goes on, growth tapers off. On the other hand, if the land is continuously grazed, good grasses are overgrazed and soil becomes bare. However, if livestock grazes intensively but briefly through small paddocks in a sequential order, consuming no more than 50% of total leaf volume, rest periods are increased and grass growth becomes more vigorous.

Image source: https://volterra.bio/en/rotational-grazing/adaptive-multi-paddock-amp-grazing-164.html
Most of the grass and water livestock consumes ends up back on the pasture as manure and urine (more evenly spread), which, together with longer rest periods, promotes greater plant and microbial diversity and complexity. More grass growing means more carbon leaking into the soil root zone to feed microbes in exchange for nutrients. Building up soil carbon improves soil porosity, permeability and holding capacity, allowing more water to infiltrate and to stay longer in the system.
In sum, the paradigm is shifted from producing livestock or grass, to manage and build up soils, as the latter, when done in the adequate way, will inevitably lead to abundant grass and healthier livestock (a focus on growing better soil, leads to growing more, better grass, which in turn the produces more and better meat faster).
In the LIFE Montado-Adapt project, this adaptation measure can be observed in the pilot areas L6 Herdade do Freixo do Meio and L5 Grupo Casablanca.


